When any business is considering a new project or investment, there must be a lot of forethought, analysis, and preparation. Key stakeholders will look at how much money they expect the investment to bring in and compare it to how much it will cost. They’ll then see if the potential profits are enough to make the project a worthwhile business decision.
How confident are you in your long term financial plan?
The project with the shortest payback period would likely be chosen. However, the payback method has some limitations, one of them being that it ignores the opportunity cost. Project managers can use the DCF model to decide which of several competing projects is likely to be more profitable and worth pursuing. However, project managers must also consider any risks involved in pursuing one project versus another.
Capital Budgeting: Features, Methods, Importance & Examples
Since the payback period does not reflect the added value of a capital budgeting decision, it is usually considered the least relevant valuation approach. However, if liquidity is a vital consideration, then payback periods are of major importance. Instead of strictly analyzing dollars and returns, payback methods of capital budgeting plan around the timing of when certain benchmarks are achieved.

Capital Budgeting: Definition, Methods, and Examples
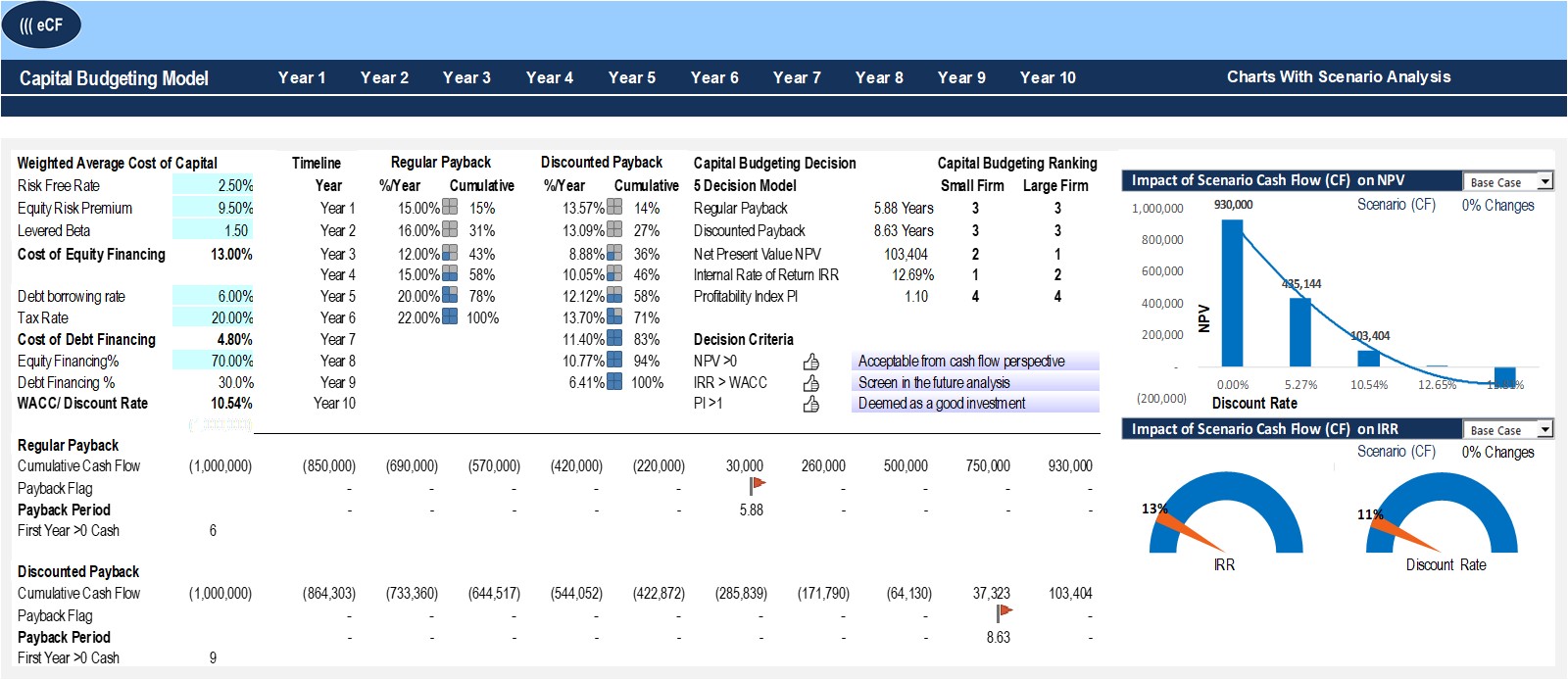
Like the internal rate of return method, the net present value method considers the time value of money. The simple rate of return for the Diamond LX model is 1.1% higher than the VIP Express model. While this is good information, especially during the initial screening phase, the simple rate of return method has limitations.
NPV also considers interest rates by considering your future earnings compared to if you invested elsewhere. While it might be easy to mentally forecast what kind of sales you could make next year, this might become more difficult when trying to project how a five or six-year $1bn investment will turn out. This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax’s permission. A financial professional will offer guidance based on the information provided and offer a no-obligation call to better understand your situation. Our goal is to deliver the most understandable and comprehensive explanations of financial topics using simple writing complemented by helpful graphics and animation videos.
Internal Rate of Return (IRR)
The company averages 35 paid guests per tour at an average revenue of $520 per guest for the bus portion of the tour. If Maya purchases the Diamond LX (35 seats), the tours would be limited to 35 paid guests law firms and client trust accounts per tour due to seat capacity. If Maya purchases the VIP Express, she estimates that she can book an average of 42 guest per tour. Maya is considering replacing the company’s tour bus with an updated model.
- Though companies are not required to prepare capital budgets, they are an integral part in planning and the long-term success of companies.
- There are other drawbacks to the payback method that include the possibility that cash investments might be needed at different stages of the project.
- Payback analysis calculates how long it will take to recoup the costs of an investment.
- The second step, exploring resource limitations, evaluates the company’s ability to invest in capital expenditures given the availability of funds and time.
- When net operating income is given, depreciation expense is added back to arrive at net cash inflow.
When considering an investment that generates revenue and costs, the annual net cash inflow is cash revenue less cash expenses. For an investment that generates cost savings and costs, the annual net cash inflow is cost savings less cash expenses. The net present value approach is the most intuitive and accurate valuation approach to capital budgeting problems. Discounting the after-tax cash flows by the weighted average cost of capital allows managers to determine whether a project will be profitable or not. And unlike the IRR method, NPVs reveal exactly how profitable a project will be in comparison with alternatives. Because a capital budget will often span many periods and potentially many years, companies often use discounted cash flow techniques to assess not only cash flow timing but also implications of the dollar.
It represents the amount the organization can realize if they sell or trade the asset at the end of its useful life. For example, Maya estimates that she can sell the Diamond LX for $54,000 in 12 years and the VIP Express for $93,000 in 10 years. Since this is a lump sum cash inflow at the end of the asset’s useful life, the discount factor is selected from the present value of a lump sum table. The Diamond LX discount factor is 0.319 taken from row 12, 10% column. The VIP Express discount factor is 0.386 taken from row 10, 10% column. The IRR for the Diamond LX model is 2% higher than the VIP Express model.



Leave a Comment